Psoriasis
OVERVIEW
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that causes your skin cells to multiply too quickly. As a result, your skin becomes itchy, flaky, and inflamed as this sped-up growth cycle interferes with the typical skin turnover process.
Psoriasis is not a contagious condition. It also cannot be spread from person-to-person contact. Instead, it occurs as a result of the overactivation of your immune system, resulting in the body attacking normal tissue.
What are the Symptoms of Psoriasis?
Common symptoms of psoriasis include:
- Itchy patches of thick skin
- Scaly, silvery, and flaky skin
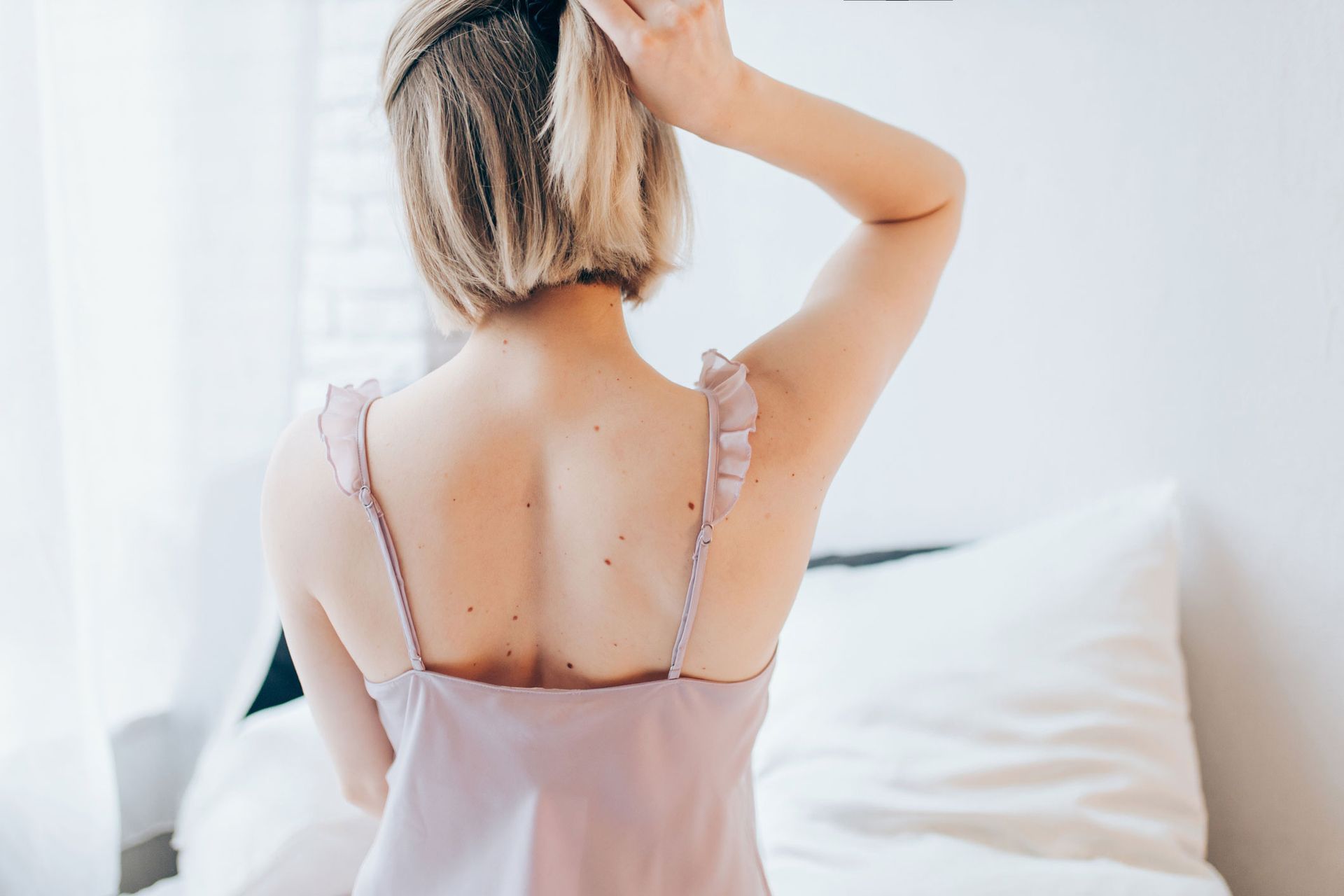
Psoriasis patches typically present themselves on your face, neck, scalp, elbows, knees, palms, and feet. However, psoriasis plaques can grow anywhere on your body.
What are the Different Types of Psoriasis?
There are several different types of psoriasis:
- Plaque psoriasis
The most commonly occurring type of psoriasis results in inflamed, red skin with white scales. - Guttate psoriasis
According to WebMD, less than 2% of all cases diagnosed are guttate psoriasis. It typically occurs most frequently in children or young adults. - Inverse psoriasis
This type of psoriasis appears on your armpits, groin, genital skin folds, and under the breasts. It is characterized by red patches of skin that are smooth but without scales or flaky. - Pustular psoriasis
An uncommon type of psoriasis results in pustules surrounded by red, inflamed skin. Pustular psoriasis is often accompanied by fever, chills, and nausea and requires immediate medical attention. - Erythrodermic psoriasis
A serious but uncommon type of psoriasis that affects a large part of your body. This results in severe itching and fiery skin that burns. Immediate medical attention is required as this severe type of psoriasis results in fluid loss, and changes to your heart rate and body temperature. - Nail psoriasis
It commonly occurs in people who have psoriatic arthritis. Results in tender nails that are yellow-brown in color with a chalk-like material under your nail beds. - Psoriatic arthritis
People with psoriatic arthritis have psoriasis along with arthritis or inflammation of the joints. Your chances of getting psoriatic arthritis increase when you have psoriasis.
How is Psoriasis Diagnosed?
Since psoriasis can look similar to other skin disorders such as eczema, getting a board-certified dermatologist to accurately diagnose your symptoms is important.
A physical exam is the first step in diagnosing your psoriasis, especially if you have scaly plaques of inflamed skin. During your appointment, a complete evaluation of your overall health and family history will also be discussed.
Your dermatologist may also recommend a skin biopsy to rule out the possibility of a skin infection.
Treatment for Psoriasis is Safe When Performed by a Board-Certified Dermatologist
A dermatologist can accurately diagnose your condition and recommend a treatment that's right for you.
Treatment of psoriasis depends on several factors, including:
- The type of psoriasis
- The amount of skin affected
- The location of the psoriatic patches
- The severity of the disease
The most common treatment options for psoriasis include:
- Topical therapies, including creams, ointments, and lotions
Used to soothe the symptoms of psoriasis, including flaky skin. - Retinoids
Formed from vitamin A, retinoids are used to slow down the growth of skin cells, and lessen swelling and redness. They may also be prescribed to patients with nail psoriasis. - Phototherapy
Involves the shining of UV light on your skin to slow down the skin cell growth process.
Biologics
These medications help decrease the chances of inflammation for people with moderate to severe psoriasis.